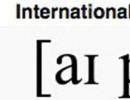The name of the caveman. Cave people. Their way of life and development. How cavemen used to live
From Greek. τρωγλοδύτης ) - since antiquity the name of wild people who lived in caves. In the 19th and 20th centuries, the term was especially applied to people who lived during the last ice age, whose remains were found in the oldest cave deposits, in layers dating back to the Paleolithic era. In colloquial speech, it is used in relation to uncultured and ignorant people.
The caves were believed to have been the main residence of Paleolithic people. It is now recognized that the Paleolithic hunter-gatherers primarily settled in open areas, and the caves were mainly used as storerooms and for ritual purposes.
In popular culture
The image of the "caveman" became widespread in popular culture, sometimes it is placed in the era of dinosaurs, such as in the cartoon The Flintstones, which is fiction.
see also
Write a review on the article "Caveman"
Notes
An excerpt characterizing the Caveman
With regard to the amusement of the people and the troops with theaters, the matter did not succeed in the same way. The theaters established in the Kremlin and in Poznyakov's house immediately closed because actresses and actors were robbed.Charity and that did not bring the desired results. False banknotes and non-false ones filled Moscow and had no price. For the French, who collected booty, they needed only gold. Not only were the counterfeit banknotes that Napoleon so graciously distributed to the unfortunate, they had no price, but silver was given below its value for gold.
But the most striking manifestation of the invalidity of the higher orders at that time was the effort of Napoleon to stop the robberies and restore discipline.
That's what the ranks of the army reported.
“Robbery continues in the city despite orders to stop it. Order has not yet been restored, and there is not a single merchant who conducts trade in a lawful manner. Only marketers allow themselves to sell, and even then stolen things.
"La partie de mon arrondissement continue a etre en proie au pillage des soldats du 3 corps, qui, non contents d"arracher aux malheureux refugies dans des souterrains le peu qui leur reste, ont meme la ferocite de les blesser a coups de sabre, comme j "en ai vu plusieurs exemples".
“Rien de nouveau outre que les soldats se permettent de voler et de piller. Le 9 October.
Caveman
The name "cave people" or troglodytes is usually given to: 1) people or peoples who use caves for living, 2) or those whose cultural remains are found in caves, 3) or, finally, those who were buried there, intentionally or accidentally. Most often, the name P. man is used in relation to those people whose remains are found in the oldest deposits of caves, in layers belonging to the Paleolithic era. Few such remains are known to date. The most remarkable are those found in the Noletskaya cave (Trou de la Nauletie) in Belgium, in the Shipka cave, in Moravia (in both cases - fragments of the lower jaws), in the Neanderthal cave (see) near Dusseldorf, in the Spy grotto, in the province of Namur (Belgium). They indicate the existence of a race of small stature, with an underdeveloped skull, a receding forehead and chin, prominent brow ridges, and a savage hunting culture reminiscent of modern Eskimo. Some believe, based on the finds of human skeletons in the caves of Truchère Furfooz in Belgium, that by the end of the Paleolithic era, another type of person appeared, with a wider skull (brachycephals); but most researchers attribute the appearance of this type to the beginning of the Neolithic era. Dolichocephaly, however, continued to predominate in this era, as evidenced by human remains from many deposits in the caves of France, England, Italy, Spain, Bohemia, Hungary and Russia; but in Germany, in the Neolithic caves of Belgium, in the tombs of the Stone Age of Prussia and Denmark, in places a rather significant percentage of brachycephals is found, which at the end of the Neolithic era, in the era of dolmens, begin to occur more and more often also in France and Switzerland. In general, it is impossible to associate the idea of a human being with the idea of a certain definite physical type and a certain stage of culture. Caves served as dwellings and burial places in the most diverse eras and among the most diverse peoples, who were at very different levels of culture - from the Paleolithic to the modern.
Encyclopedic Dictionary F.A. Brockhaus and I.A. Efron. - St. Petersburg: Brockhaus-Efron. 1890-1907 .
See what "Caveman" is in other dictionaries:
This term has other meanings, see Caveman (film). This term has other meanings, see Cavemen (film). Caveman hunt for a bear ... Wikipedia
Caveman (film, 1981) Caveman Caveman Movie poster Genre Comedy Director Carl Gottlieb Producer ... Wikipedia
Caveman (film, 1981) leading role Ringo Starr Caveman (film, 2004) ... Wikipedia
This term has other meanings, see Caveman (film). Caveman Caveman Genre Comedy Director Carl Gottlieb ... Wikipedia
This term has other meanings, see Caveman (film). Caveman Cavedweller Genre ... Wikipedia
CAVE, cave, cave. 1. adj. to the cave. Cave move. 2. Living in a cave (paleont.). Caveman (same as troglodyte). Cave bear (extinct animal of the ice age). 3. adj., by value. associated with life in caves in ... ... Explanatory Dictionary of Ushakov
CAVE, oh, oh. 1. see cave. 2. Relating to prehistoric times, to life primitive people in the caves. P. man. P. period. Cave painting (on the walls of caves.). Cave customs (translated: rough, wild). Explanatory dictionary of Ozhegov. S.I.… … Explanatory dictionary of Ozhegov
- (Ursus spelaeus) a species of bear that lived at the beginning of the modern geological era and at the end of the previous one, and whose remains are found mainly in caves, which explains the name given to this species (in this respect it is similar to the cave ... ... Encyclopedic Dictionary F.A. Brockhaus and I.A. Efron
Aya, oh. 1. to the cave. P. vault. P. move. P th organisms. P s fish. P th river. P th dwellings. 2. Relating to prehistoric times, when people lived in caves. P o art. P. man. First excavations. P. tiger. 3. Unfold Uneducated, uncivilized... encyclopedic Dictionary
caveman- oh, oh. 1) to the cave / Cave vault. Cave / rny passage. P th organisms. P s fish. P th river. P th dwellings. 2) Pertaining to prehistoric times, when people lived in caves... Dictionary of many expressions
Books
- Struggle for Fire, J. Roni Sr. Your attention is presented to the most famous stories about the life of the people of the Stone Age: "The Struggle for Fire", "The Caveman" and "Vamireh" ...
Thousands of years ago, people did not know how to build houses and therefore lived in stone caves. However, it should be noted that the very first inhabitants of the caves did not even look like us. These creatures are called Neanderthals by modern scientists.
In 1856, the remains of several people were excavated from a limestone cave in the Neander Valley in Germany. So for the first time the skeletons of primitive people were discovered, preserved entirely due to the fact that the ancient inhabitants of the caves buried their dead. As you might guess, they were called Neanderthals in honor of the Neanderthal area, where their remains were found.
According to scientists, Neanderthals lived for about 70,000 years in Central Asia, the Middle East and many regions of Europe. They appeared on Earth about 100,000 years ago.
What did a typical Neanderthal look like? He was a strong, stocky man. His face was very different from the face of a modern person: flat cheekbones, a heavy, far protruding jaw, a low forehead and an almost absent chin - such is the portrait of a normal Neanderthal. It is possible that early Neanderthals lived outdoors during the warming period between ice ages. However, after a new cold snap, they moved under the arches of the caves and learned to fight the cold.
Many hearths found in caves prove that these people used fire to keep them warm and protect them from predators. It is also very likely that they cooked food on it.
Neanderthals knew how to make not only hand axes, but also flint tools. The latter were wide fragments of stones with well-honed edges. Some of them were in the form of irregular triangles and, apparently, were used as knives for skinning and cutting the meat of slaughtered animals. It is possible that Neanderthal hunters also had wooden spears pointed at the end.
And, finally, one very interesting detail about the Neanderthals: their brains were larger than the brains of modern humans!
At the end of the ice age, the Cro-Magnons - the descendants of the Neanderthals, whose appearance was already much more similar to the appearance of modern people - began to move to Europe. They are so named only because the remains of these cave dwellers were found in the town of Cro-Magnon in southern France. Also interesting is the fact that specialists who studied the remains, the skeletons of these cave dwellers, found that they were quite civilized and smart people. If they lived today, they could become scientists, statesmen or businessmen.
These people lived in turbulent times, surrounded by wild animals and other dangers. But despite this, they found time to make beautiful drawings on the walls of the caves. These drawings have survived to our time, are well preserved and delight us with their beauty and skillful technique.
These people had a well-developed social life. They lived in families. But since they began to hunt in groups, they had to unite in tribes. They believed in the afterlife: that the dead could be resurrected and reborn in the other world.
Gradually they created more advanced stone tools and new weapons. They learned how to carve a spear and a harpoon from horn and bone. They also invented arrows for guns. Women learned how to process skins and sew clothes from them with bone needles. As we can see, these people had intelligence and reached a high stage of development.
The name "cave people" or troglodytes is usually given to: 1) people or peoples who use caves for living, 2) or those whose cultural remains are found in caves, 3) or, finally, those who were buried there, intentionally or accidentally. Most often, the name P. man is used in relation to those people whose remains are found in the oldest deposits of caves, in layers belonging to the Paleolithic era. Few such remains are known to date. The most remarkable are those found in the Noletskaya cave (Trou de la Nauletie) in Belgium, in the Shipka cave, in Moravia (in both cases - fragments of the lower jaws), in the Neanderthal cave (see) near Dusseldorf, in the Spy grotto, in the province of Namur (Belgium). They indicate the existence of a race of small stature, with an underdeveloped skull, a receding forehead and chin, prominent brow ridges, and a savage hunting culture reminiscent of modern Eskimo. Some believe, based on the finds of human skeletons in the caves of Truchère Furfooz in Belgium, that by the end of the Paleolithic era, another type of person appeared, with a wider skull (brachycephals); but most researchers attribute the appearance of this type to the beginning of the Neolithic era. Dolichocephaly, however, continued to predominate in this era, as evidenced by human remains from many deposits in the caves of France, England, Italy, Spain, Bohemia, Hungary and Russia; but in Germany, in the Neolithic caves of Belgium, in the tombs of the Stone Age of Prussia and Denmark, in places a rather significant percentage of brachycephals is found, which at the end of the Neolithic era, in the era of dolmens, begin to occur more and more often also in France and Switzerland. In general, it is impossible to associate the idea of a human being with the idea of a certain definite physical type and a certain stage of culture. Caves served as dwellings and burial places in the most diverse eras and among the most diverse peoples, who were at very different levels of culture - from the Paleolithic to the modern.
- - located on the right bank of the Chernaya River at its confluence with the Northern Bay of Sevastopol ...
Toponymic Dictionary of Crimea
- - is located on the outskirts of Bakhchisaray, on the western slope of the Mairam-Dere gorge. There are two versions of the founding of the monastery...
Toponymic Dictionary of Crimea
- - This is the modern name of the monastery, formerly known as Ctenus, Kalamita...
- - It was located in the Middle Ages in a remote, protected by nature place - in the Balaklava region, 12 km. east-southeast of the top of the Sevastopol Bay and two km. northwest of the village of Ternovka in the caves...
Toponymic Dictionary of Sevastopol
- - an extinct predatory mammal of the family. feline. Lived in the 2nd floor. Pleistocene - early. Holocene, in Europe and North. Asia. The size of a large lion or tiger. He lived not in caves, but on the plains and in the foothills...
-
Natural science. encyclopedic Dictionary
- - a species of bear that lived at the beginning of the modern geological era and at the end of the previous one, and whose remains are found mainly in caves, which explains the name given to this species and the cave hyena - Hyaena ...
Encyclopedic Dictionary of Brockhaus and Euphron
- - an extinct predatory mammal of the cat family ...
Great Soviet Encyclopedia
- - an extinct predatory mammal of the cat family. Lived in the 2nd floor. Pleistocene - early Holocene, in Europe and North. Asia. The size of a large lion or tiger. He lived not in caves, but on the plains and in the foothills...
- - an extinct carnivorous mammal. Lived in the Pleistocene, in Eurasia. In terms of body structure, it is close to the brown bear, but much larger. Lived in caves...
- - Working with fuels and lubricants and mechanisms is not the best way to maintain personal hygiene. Representatives of other professions sometimes apply for the place of a tanker ...
Dictionary of folk phraseology
- - Bo/g-human/k,...
merged. Separately. Through a hyphen. Dictionary-reference
- - cave adj. 1. ratio with noun. cave associated with it 2. Peculiar to the cave, characteristic of it. 3. Belonging to a cave. 4. Located in a cave. 5...
Explanatory Dictionary of Efremova
- - ...
Spelling Dictionary
- - about an internally and externally beautiful person Cf. Nature, as Shakespeare says, could point her finger at him and say: Tall, slender figure, noble posture and this, I don’t know, is something attractive in the face .....
Explanatory-phraseological dictionary of Michelson
- - A Russian person is a kind person...
IN AND. Dal. Proverbs of the Russian people
"Caveman" in the books
From the book The Disappeared World author Akimushkin Igor Ivanovich"Cave" lion and cave bear
From the book The Disappeared World author Akimushkin Igor Ivanovich"Cave" lion and cave bear There was a time when lions lived not only throughout Africa, but also on the Arabian Peninsula, in Persia, northwestern India and even in Turkey, Greece, the Caucasus and in the lower reaches of the Don! Drawings and bones of cave scientists found lions in the grottoes of Spain,
CAVE STALINISM
From the book Forbidden Truth by Viktor Suvorov author Pronin AlexanderCAVE STALINISM One of the elements of the USSR's preparation for war, which predetermined its brutal character, was the creation of a legislative framework to prevent soldiers from being captured by the enemy. Measures were taken ahead of time. According to researcher Svetlana Malygina,
Caveman
From the book The Great Delusions of Mankind. 100 Immutable Truths Everyone Believed In authorCaveman It is believed that ancient man lived in natural shelters - caves and grottoes. However, this is not quite true. Scientists believe that ancient people really visited the caves (as evidenced by wall paintings), but they did not live in them.
Cave World
From the book Update August 30, 2003 author Pyatibrat VladimirCave World Caucasus - white mountains - In all regions of the world, Atlantis builds and equips underground cities. Many underground halls are being built in the center of Oceania. Ancient Slavic cities were built under the current shelf of the Black Sea, with more a high degree
Cave labyrinth Gortyna
From the book Great Secrets of Civilizations. 100 stories about the mysteries of civilizations author Mansurova TatianaGortyna cave labyrinth Oxford researchers worked together with experts from the Hellenic Speleological Society. They discovered that black archaeologists had already visited here before them, who wanted to blow up one of the caves in the hope of finding a hidden room with
cave monastery
From the book Secrets of the Mountain Crimea author Fadeeva Tatyana MikhailovnaCave Monastery The most interesting cave church of Mangup is located above the main road to the eastern gate: a secret exit from the city led to it through a cleft in the rocks. The natural grotto in front of the temple was used as a courtyard; opposite were the cells
Kailasanath cave temple in Ellur
From the book 100 famous monuments of architecture author Pernatiev Yury SergeevichKailasanatha Cave Temple in Ellur Rock temples and structures are a special type of architecture that is not inferior in its uniqueness to European urban masterpieces. The history of the construction of such monuments dates back several hundred years before
Caveman
From the book The Complete Encyclopedia of Our Delusions author Mazurkevich Sergey AlexandrovichCaveman
From The Complete Illustrated Encyclopedia of Our Delusions [with transparent pictures] author Mazurkevich Sergey AlexandrovichCaveman It is generally accepted that ancient man lived in natural shelters - caves and grottoes. However, this is not quite true. Scientists believe that ancient people really visited caves (as evidenced by wall paintings), but they did not live in them.
Caveman
From the book The Complete Illustrated Encyclopedia of Our Delusions [with illustrations] author Mazurkevich Sergey AlexandrovichCaveman It is generally accepted that ancient man lived in natural shelters - caves and grottoes. However, this is not quite true. Scientists believe that ancient people really visited caves (as evidenced by wall paintings), but they did not live in them.
cave lion
From the book Big Soviet Encyclopedia(PE) author TSBGarni and cave monastery Geghard
From the book Journey through Soviet Armenia author Shahinyan MariettaGarni and cave monastery Geghard Over the gorge of Garni (ancient Azat) there is a castle, “a strong fortress”, according to Moses Khorensky. There, ten centuries ago, in the same autumn, exhausted by jealousy, Queen Saakanush, the yearning wife of Ashot, looked for hours at the Dvina road.
Chapter 1
From book 4 secrets life success author Tsiporkina Inessa VladimirovnaChapter 1. Caveman of the third millennium All this is in my blood For hundreds and hundreds of years, medicine has tried to separate the body and soul - and treat each object separately. For all that, the human race, stubborn in its ignorance, did not want to forget the ancient sciences (or,
Chapter 2 The Caveman Counts Carbohydrates
From the book Chinese Study in Practice [Simple Transition to a Healthy Lifestyle] by Campbell ThomasChapter 2 The Caveman Counts Carbohydrates Where is the 360 kg gorilla sitting? Of course, wherever you want. Gorillas are one of the most powerful herbivores on the planet. Like other primates, they get most of their energy from plants: green leaves, stems, fruits, and vines. But