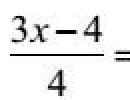All necessary formulas in chemistry. Chemical formulas – Knowledge Hypermarket
several basic concepts and formulas.
All substances have different mass, density and volume. A piece of metal from one element can weigh many times more than an exactly the same size piece of another metal.
Mole(number of moles)
designation: mole, international: mol- a unit of measurement for the amount of a substance. Corresponds to the amount of substance that contains N.A. particles (molecules, atoms, ions) Therefore, a universal quantity was introduced - number of moles. A frequently encountered phrase in tasks is “received... mole of substance"
N.A.= 6.02 1023
N.A.- Avogadro's number. Also “a number by agreement.” How many atoms are there in the tip of a pencil? About a thousand. It is not convenient to operate with such quantities. Therefore, chemists and physicists around the world agreed - let’s designate 6.02 × 1023 particles (atoms, molecules, ions) as 1 mole substances.
1 mole = 6.02 1023 particles
This was the first of the basic formulas for solving problems.
Molar mass of a substance
Molar mass substance is the mass of one mole of substance.
Denoted as Mr. It is found according to the periodic table - it is simply the sum of the atomic masses of a substance.
For example, we are given sulfuric acid- H2SO4. Let's count molar mass substances: atomic mass H = 1, S-32, O-16.
Mr(H2SO4)=1 2+32+16 4=98 g\mol.
The second necessary formula for solving problems is
substance mass formula:
That is, to find the mass of a substance, you need to know the number of moles (n), and we find the molar mass from the Periodic Table.
Law of conservation of mass - The mass of substances that enter into a chemical reaction is always equal to the mass of the resulting substances.
If we know the mass(es) of the substances that reacted, we can find the mass(es) of the products of that reaction. And vice versa.
The third formula for solving chemistry problems is
volume of substance:
Sorry, this image does not meet our guidelines. To continue publishing, please delete the image or upload another one.Where did the number 22.4 come from? From Avogadro's law:
V equal volumes Different gases taken at the same temperature and pressure contain the same number of molecules.
According to Avogadro's law, 1 mole of an ideal gas under normal conditions (n.s.) has the same volume Vm= 22.413 996(39) l
That is, if in the problem we are given normal conditions, then, knowing the number of moles (n), we can find the volume of the substance.
So, basic formulas for solving problems in chemistry
Avogadro's numberN.A.
6.02 1023 particles
Quantity of substance n (mol)
n=V\22.4 (l\mol)
Mass of substance m (g)
Volume of substance V(l)
V=n 22.4 (l\mol)
Sorry, this image does not meet our guidelines. To continue publishing, please delete the image or upload another one.These are formulas. Often, to solve problems, you first need to write the reaction equation and (required!) arrange the coefficients - their ratio determines the ratio of moles in the process.
Key words: Chemistry 8th grade. All formulas and definitions, symbols physical quantities, units of measurement, prefixes to designate units of measurement, relationships between units, chemical formulas, basic definitions, briefly, tables, diagrams.
1. Symbols, names and units of measurement
some physical quantities used in chemistry
| Physical quantity | Designation | Unit |
| Time | t | With |
| Pressure | p | Pa, kPa |
| Quantity of substance | ν | mole |
| Mass of substance | m | kg, g |
| Mass fraction | ω | Dimensionless |
| Molar mass | M | kg/mol, g/mol |
| Molar volume | Vn | m 3 /mol, l/mol |
| Volume of substance | V | m 3, l |
| Volume fraction | Dimensionless | |
| Relative atomic mass | A r | Dimensionless |
| Mr | Dimensionless | |
| Relative density of gas A to gas B | D B (A) | Dimensionless |
| Density of matter | R | kg/m 3, g/cm 3, g/ml |
| Avogadro's constant | N A | 1/mol |
| Absolute temperature | T | K (Kelvin) |
| Temperature in Celsius | t | °C (degrees Celsius) |
| Thermal effect chemical reaction | Q | kJ/mol |

2. Relationships between units of physical quantities

3. Chemical formulas in 8th grade
4. Basic definitions in 8th grade

- Atom- the smallest chemically indivisible particle of a substance.
- Chemical element - certain type atoms.
- Molecule- the smallest particle of a substance that retains its composition and Chemical properties and consisting of atoms.
- Simple substances- substances whose molecules consist of atoms of the same type.
- Complex substances- substances whose molecules consist of atoms of different types.
- Qualitative composition of the substance shows which atoms of elements it consists of.
- Quantitative composition of the substance shows the number of atoms of each element in its composition.
- Chemical formula- conditional recording of the qualitative and quantitative composition of a substance using chemical symbols and indexes.
- Atomic mass unit(amu) - a unit of measurement of atomic mass, equal to the mass of 1/12 of a carbon atom 12 C.
- Mole- the amount of substance that contains the number of particles, equal to the number atoms in 0.012 kg of carbon 12 C.
- Avogadro's constant (Na = 6*10 23 mol -1) - the number of particles contained in one mole.
- Molar mass of a substance (M ) is the mass of a substance taken in an amount of 1 mole.
- Relative atomic mass element A r - the ratio of the mass of an atom of a given element m 0 to 1/12 of the mass of a carbon atom 12 C.
- Relative molecular weight substances M r - the ratio of the mass of a molecule of a given substance to 1/12 of the mass of a carbon atom 12 C. The relative molecular mass is equal to the sum of the relative atomic masses chemical elements forming a compound, taking into account the number of atoms of a given element.
- Mass fraction chemical element ω(X) shows which part of the relative molecular weight substance X falls on a given element.
ATOMIC-MOLECULAR TEACHING
1. There are substances with molecular and non-molecular structure.
2. There are gaps between the molecules, the sizes of which depend on the state of aggregation of the substance and temperature.
3. Molecules are in continuous motion.
4. Molecules are made up of atoms.
6. Atoms are characterized by a certain mass and size.
At physical phenomena molecules are preserved, but are usually destroyed by chemical reactions. Atoms at chemical phenomena rearrange to form molecules of new substances.

LAW OF CONSTANT COMPOSITION OF MATTER
Each chemically pure substance of molecular structure, regardless of the method of preparation, has a constant qualitative and quantitative composition.
VALENCE
Valence is the property of an atom of a chemical element to attach or replace a certain number of atoms of another element.

CHEMICAL REACTION
A chemical reaction is a phenomenon as a result of which other substances are formed from one substance. Reactants are substances that enter into a chemical reaction. Reaction products are substances formed as a result of a reaction.
Signs of chemical reactions:
1. Release of heat (light).
2. Change in color.
3. Odor appears.
4. Formation of sediment.
5. Gas release.
>> Chemical formulas
Chemical formulas
The material in this paragraph will help you:
> find out what the chemical formula is;
> read the formulas of substances, atoms, molecules, ions;
> use the term “formula unit” correctly;
> compose chemical formulas of ionic compounds;
> characterize the composition of a substance, molecule, ion using a chemical formula.
Chemical formula.
Everyone has it substances there is a name. However, by its name it is impossible to determine what particles a substance consists of, how many and what kind of atoms are contained in its molecules, ions, and what charges the ions have. The answers to such questions are given by a special record - a chemical formula.
A chemical formula is the designation of an atom, molecule, ion or substance using symbols chemical elements and indexes.
The chemical formula of an atom is the symbol of the corresponding element. For example, the Aluminum atom is designated by the symbol Al, the Silicon atom by the symbol Si. Simple substances also have such formulas - metal, aluminum, non-metal atomic structure silicon.
Chemical formula molecules of a simple substance contains the symbol of the corresponding element and the subscript - a small number written below and to the right. The index indicates the number of atoms in the molecule.
An oxygen molecule consists of two oxygen atoms. Its chemical formula is O 2. This formula is read by first pronouncing the symbol of the element, then the index: “o-two”. The formula O2 denotes not only the molecule, but also the substance oxygen itself.
The O2 molecule is called diatomic. Of similar molecules (their general formula- E 2) consist of simple substances Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Fluor, Chlorine, Bromine, Iodine.
Ozone contains three-atomic molecules, white phosphorus contains four-atomic molecules, and sulfur contains eight-atomic molecules. (Write the chemical formulas of these molecules.)
H 2
O2
N 2
Cl2
BR 2
I 2
In the formula of a molecule of a complex substance, the symbols of the elements whose atoms are contained in it, as well as indices, are written down. Molecule carbon dioxide consists of three atoms: one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. Its chemical formula is CO 2 (read “tse-o-two”). Remember: if a molecule contains one atom of any element, then the corresponding index, i.e. I, is not written in the chemical formula. The formula of a carbon dioxide molecule is also the formula of the substance itself.
In the formula of an ion, its charge is additionally written down. To do this, use a superscript. It indicates the amount of charge with a number (they do not write one), and then a sign (plus or minus). For example, a Sodium ion with a charge +1 has the formula Na + (read “sodium-plus”), a Chlorine ion with a charge - I - SG - (“chlorine-minus”), a hydroxide ion with a charge - I - OH - (“ o-ash-minus"), a carbonate ion with a charge -2 - CO 2- 3 (“ce-o-three-two-minus”).
Na+,Cl-
simple ions
OH - , CO 2- 3
complex ions
In the formulas of ionic compounds, first write down, without indicating charges, positively charged ions, and then - negatively charged (Table 2). If the formula is correct, then the sum of the charges of all ions in it is zero.
table 2
Formulas of some ionic compounds
In some chemical formulas a group of atoms or a complex ion is written in parentheses. As an example, let's take the formula of slaked lime Ca(OH) 2. This is an ionic compound. In it, for every Ca 2+ ion there are two OH - ions. The formula of the compound reads " calcium-o-ash-twice”, but not “calcium-o-ash-two”.
Sometimes in chemical formulas, instead of symbols of elements, “foreign” letters, as well as index letters, are written. Such formulas are often called general. Examples of formulas of this type: ECI n, E n O m, F x O y. First
the formula denotes a group of compounds of elements with Chlorine, the second - a group of compounds of elements with Oxygen, and the third is used if the chemical formula of a compound of Ferrum with Oxygen unknown and
it should be installed.
If you need to designate two separate Neon atoms, two oxygen molecules, two carbon dioxide molecules or two Sodium ions, use the notations 2Ne, 20 2, 2C0 2, 2Na +. The number in front of the chemical formula is called the coefficient. Coefficient I, like index I, is not written.
Formula unit.
What does the notation 2NaCl mean? NaCl molecules do not exist; table salt is an ionic compound that consists of Na + and Cl - ions. A pair of these ions is called the formula unit of a substance (it is highlighted in Fig. 44, a). Thus, the notation 2NaCl represents two formula units of table salt, i.e., two pairs of Na + and C l- ions.
The term “formula unit” is used for complex substances not only of ionic but also of atomic structure. For example, the formula unit for quartz SiO 2 is the combination of one Silicium atom and two Oxygen atoms (Fig. 44, b).

Rice. 44. formula units in compounds of ionic (a) atomic structure (b)
A formula unit is the smallest “building block” of a substance, its smallest repeating fragment. This fragment can be an atom (in a simple substance), molecule(in a simple or complex substance),
a collection of atoms or ions (in a complex substance).
Exercise. Draw up the chemical formula of a compound that contains Li + i SO 2- 4 ions. Name the formula unit of this substance.
Solution
In an ionic compound, the sum of the charges of all ions is zero. This is possible provided that for each SO 2- 4 ion there are two Li + ions. Hence the formula of the compound is Li 2 SO 4.
The formula unit of a substance is three ions: two Li + ions and one SO 2- 4 ion.
Qualitative and quantitative composition of a substance.
A chemical formula contains information about the composition of a particle or substance. Characterizing high-quality composition, call the elements that form a particle or substance, and when characterizing the quantitative composition, indicate:
The number of atoms of each element in a molecule or complex ion;
the ratio of atoms of different elements or ions in a substance.
Exercise. Describe the composition of methane CH 4 (molecular compound) and soda ash Na 2 CO 3 (ionic compound)
Solution
Methane is formed by the elements Carbon and Hydrogen (this is a qualitative composition). A methane molecule contains one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms; their ratio in the molecule and in the substance
N(C): N(H) = 1:4 (quantitative composition).
(The letter N denotes the number of particles - atoms, molecules, ions.
Soda ash is formed by three elements - Sodium, Carbon and Oxygen. It contains positively charged Na + ions, since Sodium is a metallic element, and negatively charged CO -2 3 ions (qualitative composition).
The ratio of atoms of elements and ions in a substance is as follows:
conclusions
A chemical formula is a recording of an atom, molecule, ion, substance using symbols of chemical elements and indices. The number of atoms of each element is indicated in the formula using a subscript, and the charge of the ion is indicated by a superscript.
Formula unit is a particle or collection of particles of a substance represented by its chemical formula.
The chemical formula reflects the qualitative and quantitative composition of a particle or substance.
?
66. What information about a substance or particle does a chemical formula contain?
67. What is the difference between a coefficient and a subscript in chemical notation? Complete your answer with examples. What is the superscript used for?
68. Read the formulas: P 4, KHCO 3, AI 2 (SO 4) 3, Fe(OH) 2 NO 3, Ag +, NH + 4, CIO - 4.
69. What do the entries mean: 3H 2 0, 2H, 2H 2, N 2, Li, 4Cu, Zn 2+, 50 2-, NO - 3, 3Ca(0H) 2, 2CaC0 3?
70. Write down chemical formulas that read like this: es-o-three; boron-two-o-three; ash-en-o-two; chrome-o-ash-thrice; sodium-ash-es-o-four; en-ash-four-double-es; barium-two-plus; pe-o-four-three-minus.
71. Make up the chemical formula of a molecule that contains: a) one Nitrogen atom and three Hydrogen atoms; b) four atoms of Hydrogen, two atoms of Phosphorus and seven atoms of Oxygen.
72. What is the formula unit: a) for soda ash Na 2 CO 3 ; b) for the ionic compound Li 3 N; c) for the compound B 2 O 3, which has an atomic structure?
73. Make up formulas for all substances that can only contain the following ions: K + , Mg2 + , F - , SO -2 4 , OH - .
74. Describe the qualitative and quantitative composition of:
a) molecular substances - chlorine Cl 2, hydrogen peroxide (hydrogen peroxide) H 2 O 2, glucose C 6 H 12 O 6;
b) ionic substance - sodium sulfate Na 2 SO 4;
c) ions H 3 O +, HPO 2- 4.
Popel P. P., Kryklya L. S., Chemistry: Pidruch. for 7th grade zagalnosvit. navch. closing - K.: VC "Academy", 2008. - 136 p.: ill.
Lesson content lesson outline and supporting frame lesson presentation interactive technologies accelerator teaching methods Practice tests, testing online tasks and exercises homework workshops and trainings questions for class discussions Illustrations video and audio materials photographs, pictures, graphs, tables, diagrams, comics, parables, sayings, crosswords, anecdotes, jokes, quotes Add-ons abstracts cheat sheets tips for the curious articles (MAN) literature basic and additional dictionary of terms Improving textbooks and lessons correcting errors in the textbook, replacing outdated knowledge with new ones Only for teachers calendar plans learning programs guidelinesCheck information. It is necessary to check the accuracy of the facts and reliability of the information presented in this article. On the talk page there is a discussion on the topic: Doubts regarding terminology. Chemical formula ... Wikipedia
A chemical formula reflects information about the composition and structure of substances using chemical symbols, numbers and dividing symbols of brackets. Currently, the following types of chemical formulas are distinguished: The simplest formula. Can be obtained by experienced... ... Wikipedia
A chemical formula reflects information about the composition and structure of substances using chemical symbols, numbers and dividing symbols of brackets. Currently, the following types of chemical formulas are distinguished: The simplest formula. Can be obtained by experienced... ... Wikipedia
A chemical formula reflects information about the composition and structure of substances using chemical symbols, numbers and dividing symbols of brackets. Currently, the following types of chemical formulas are distinguished: The simplest formula. Can be obtained by experienced... ... Wikipedia
A chemical formula reflects information about the composition and structure of substances using chemical symbols, numbers and dividing symbols of brackets. Currently, the following types of chemical formulas are distinguished: The simplest formula. Can be obtained by experienced... ... Wikipedia
Main article: List of inorganic compounds inorganic compounds by element, an informational list of inorganic compounds, presented in alphabetical order (by formula) for each substance, hydrogen acids of elements (if ... ... Wikipedia
This article or section needs revision. Please improve the article in accordance with the rules for writing articles... Wikipedia
A chemical equation (equation of a chemical reaction) is a conventional representation of a chemical reaction using chemical formulas, numerical coefficients and mathematical symbols. The equation of a chemical reaction gives qualitative and quantitative... ... Wikipedia
Chemical software are computer programs used in the field of chemistry. Contents 1 Chemical editors 2 Platforms 3 Literature ... Wikipedia
Books
- Japanese-English-Russian dictionary for installation of industrial equipment. About 8,000 terms, Popova I.S. The dictionary is intended for a wide range of users and primarily for translators and technical specialists involved in the supply and implementation of industrial equipment from Japan or...
- A brief dictionary of biochemical terms, Kunizhev S.M.. The dictionary is intended for students of chemical and biological specialties at universities studying a course in general biochemistry, ecology and fundamentals of biotechnology, and can also be used in ...