Presentation of a lesson on the surrounding world “Shapes of the earth’s surface” (grade 2). Presentation of a lesson on the surrounding world “Shapes of the earth’s surface” (grade 2) Mountains are very convenient for farming
Tatiana Norinskaya
"Shapes of the Earth's Surface." Summary of an open lesson on the world around us in 2nd grade (School of Russia program)
Summary of an open lesson on the world around us in 2nd grade
(program School of Russia)
Teacher: Norinskaya Tatyana Aleksandrovna
Subject lesson: Shapes of the earth's surface.
Type lesson: Learning new material.
Goals lesson:
1. Didactic:
give children the concept of basic shapes of the earth's surface;
introduce the structure of hills and mountains;
introduce students to types of reservoirs;
teach to distinguish parts of the river (source, mouth, channel, banks);
compare river and lake.
2. Developmental:
promote the development of creative, logical thinking based on observation and comparison.
3. Educational:
to cultivate a sense of belonging to the small Motherland through studying the nature of the native land; develop an environmental attitude towards to the surrounding world.
During the classes.
Organizing time
The bell rang
The children stood on lesson
Today on our there are guests in the lesson.
Let's welcome them.
Sit down.
Checking homework
The teacher gives cards for independent work to three pairs of students in each row. Students prepare answers and then answer.
CARD#1
EXERCISE:
1. EXPLAIN WHAT IS A HORIZON?
2. WHAT IS A HORIZON LINE?
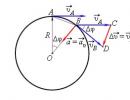
3. ADD TO THE FIGURE-DIAGRAM THE NAMES OF THE HORIZON SIDES. EXPLAIN HOW THE SIDES OF THE HORIZON ARE POSITIONED RELATIVE TO EACH OTHER.
CARD#2
EXERCISE:
1. WHAT IS THE DEVICE FOR DETERMINING THE SIDES OF THE HORIZON CALLED?
2. NAME AND SIGN WHAT PARTS IT CONSISTS OF?
CARD#3
EXERCISE:
NAME BY WHAT NATURAL FEATURES CAN YOU DETERMINE THE SIDES OF THE HORIZON?
The rest of the children complete the teacher’s assignment on checkered pieces of paper.
Draw the traveler's route if 1 cell is the path that the traveler covers in 1 hour:
“The traveler left point A and walked north for 2 hours, then 2 hours to the west, 2 hours to the north and 2 hours to the east. Then he stopped (point B on the diagram) and went further: 1 hour went north, 1 hour east, 2 hours south and 3 hours east. Here he spent the night (point C). I went in the morning further: 1 hour to the north, 1 hour to the east, 4 hours to the south and 2 hours to the west. The traveler was tired and stopped (point D). Then he went further: 2 hours to the north, 1 hour to the west, 2 hours to the south, 2 hours to the west... And returned home.
At the end of the work, there is a self-test, then those sitting at the desk exchange notebooks. Mutual verification is carried out.
Who rated themselves the highest?
Who's in the middle?
Who is not happy with their job?
Students who prepared using cards answer.
Statement of a problematic question
Open textbook on pages 90-91. There is a map in front of you. What is it called? (physical card Russia)
What can you tell us about this map? (blue – oceans, seas, rivers, lakes; green – plains; brown – mountains) Find and name rivers, seas, oceans.
I will name the objects on the map, and you will look carefully and think about what the topic of today will be lesson. (East European Plain, West Siberian Plain, Ural Mountains)
What do you think the topic will be? lesson? (mountains and plains)
Yes. Subject lesson - shapes of the earth's surface. Slide1
Work on the topic lesson.
Guess the riddle: Grandma wears a snow hat.
The stone sides are shrouded in clouds. (mountain) Slide2
Try to explain what mountains are? (children's answers) Slide3
You rarely see a single mountain; most often the mountains are located in rows and they are called mountain ranges. Slide4
How can you explain what plains are? Slide5
Physical education.
The wind blows in our faces
The tree swayed
The wind is getting quieter, quieter
The tree is getting higher and higher
Continuation of work on the topic lesson.
Plains are flat and hilly.
Explain why the plains received such a name? Slide6
The elevations on the plain are hills. Slide7
But, in addition, on the plains there are depressions with steep slopes - these are ravines. Slide8
If the hill and mountain rise above earth's surface, can we conclude that these are the same thing? (children's answers) Slide9
Work according to the textbook.
Open textbook on page 79.
Look at the diagram and tell me what are the similarities between a mountain and a hill? Slide10
Name the parts of the hill.
Name the parts of the mountain.
What can be concluded?
Let's consider more details: base is where a hill or mountain begins; summit – the highest part of a hill or mountain; slope is the part of a hill or mountain that is located between the base and the top. Slopes can be steep or gentle. Slide 11
What is the difference between a hill and a mountain? Slide12
What types of mountains are there? Slide13
Open page 80-81. Let's read aloud the story of Nikolai Ivanovich Sladkov "The Beauty of the Mountains" (read)
What struck and surprised you about this story? Slide14
Work in a notebook.
Open notebook on page 32. Label the parts of the hill. Self-test. Peer review. (children check each other’s work and give marks)
Who hasn't made a single mistake?
Who made 1-2 mistakes? What mistakes were made?
Who made more than 2 mistakes?
Everyone did a fairly good job with this task. Those who made mistakes have the opportunity to carefully familiarize themselves with this topic at home and at the next lesson successfully complete the test.
Bottom line lesson. Reflection.
With which you got acquainted with the shapes of the earth's surface(mountains and plains)
What types of plains are there? (flat and hilly) Slide15
Which the shape of the earth's surface is called a hill(elevations on the plain)
Which the shape of the earth's surface is called a ravine(recesses with steep slopes)
Who's working on lesson rated the highest?
Who rated themselves as average? What didn't work?
Who's on the low side? Why?
What new did you learn?
On lesson you all did a good job and I am very pleased with your work.
Ratings for lesson….
Homework.
Open diaries and write down homework
Textbook page 78-81, notebook 32
Lesson is over. thanks for lesson.
Sections: Primary School
Lesson duration: 35 minutes
Class: 2
Lesson objectives:
- Students learning new material on the topic of the lesson and consolidating the acquired knowledge
- Formation of ideas about the shapes of the earth's surface.
- Formation of an emotionally positive attitude towards the subject.
Lesson objectives:
Educational:
- Introduce children to the basic shapes of the earth's surface; with the structure of hills and mountains.
Educational:
- To develop children’s cognitive activity, the ability to express their thoughts, and reason.
- Developing the ability to analyze and draw conclusions, defend one’s point of view, and the ability to apply accumulated knowledge;
- Expand children's horizons.
Educational:
- To foster an environmental culture among schoolchildren.
- To cultivate love and respect for the nature of the native land.
- Place of the lesson in the curriculum: Lesson 3 on the topic “Travel”.
- Methodological techniques: verbal (conversation, story), visual and demonstration: (video method, explanatory and illustrative).
- Lesson type: lesson on learning new material .
- Forms of work in the lesson: independent, frontal, work in pairs.
Lesson equipment:
Hardware: personal computer, demonstration screen, multimedia projector, scanner, printer .
Software: Microsoft PowerPoint, Word, CD "Geography of Russia. Nature and population."
Literature: Textbook by A.A. Pleshakov “The World Around Us” 2nd grade, workbook “The World Around Us” author A.A. Pleshakov, A. Dietrich "Why", M. "Pedagogy", 2000, "Children's Encyclopedia. Earth", M., "Pedagogy", 2002.
During the classes
I. Organizational moment.
Well, check it out, my friend,
Are you ready to start the lesson?
Is everything in place?
Is everything alright?
Pen, book and notebooks?
Is everyone sitting correctly?
Is everyone watching carefully?
Interesting questions
Daredevils are awaited.
I wish them good luck.
Come out!
Who's ready?
II. Checking homework.
The teacher gives three students cards for independent work. Students prepare answers and then respond. Checking is carried out using slides.
Card 1
- Explain what a horizon is?
- What is a horizon line? Show the horizon line in the drawing. Slide 2. (The line becomes dotted)
- Add the names of the sides of the horizon to the diagram. Explain how the sides of the horizon are positioned relative to each other. Slide 2. (The names of the sides of the horizon appear.)
Card 2
- The card comes with a compass. What is the name of the device for determining the sides of the horizon?
- Name and show what parts it consists of. Explain and show how to use it. Slide 3. (Drawing of a compass, fuse, magnetic needle, body).
Card 3
Tell us how you can determine the sides of the horizon without a compass using local signs of "Terrain Orientation." Slide 4. (Natural signs of terrain orientation.)
The rest of the children complete the teacher’s assignments in their notebooks.
Draw the traveler's route if 1 cell is the path that the traveler covers in 1 hour:
“The traveler left point A and walked north for two hours, then 2 hours to the west, 2 hours to the north and 2 hours to the east. Then he made a stop (point B on the diagram) and went further: 1 hour walked north, 1 hour to the east, 2 hours to the south and 3 hours to the east. Here he spent the night (point C). In the morning he went further: 1 hour to the north, 1 hour to the east, 4 hours to the south and 2 hours to the west. The traveler got tired and stopped at point D. Then he went further: he walked north for 2 hours, west for 1 hour, south for 2 hours, west for 2 hours... And returned home.
At the end of work, children sitting at the same desk exchange notebooks. Mutual verification is carried out. Then the answers of the children working with individual cards are heard and evaluated.
III. Lesson topic message.
(A prepared student reads a poem)
My land is my land
Dear spaces!
My land, how great you are!
From border to border.
And a fast train straight ahead
It won't finish in a week.
Look at slide 5, there is a physical map of Russia in front of you. Images, what color do you see on it? (Blue, yellow, green.) What do you think is indicated on the physical map, blue or cyan, brown and green? (Seas, lakes, rivers, mountains, plains.)
This is what the plains and mountains look like on the map. Today in the lesson we will talk about the surface shapes of our country, we will learn to find and distinguish them on the map. Slide 6. (Lesson topic)
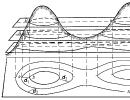
Now look at the images on the slides. Slide 7. (Plain and mountains.) Here you can see the main forms of the earth's surface - plains and mountains. Try to explain what it is. (Children try to explain why they are named that way.)
What part of the earth's surface do you think is called a plain? (Flat.) Slide 8. (Image of a plain and definition.)
A plain is a flat area of the earth's surface, occupying a large area and having slight differences in height.
The teacher shows a slide with a picture of "The Hilly and Flat Plains." Slide 9. On the slide you see images of two plains, try to determine how they differ? (Height).
Plains are flat and hilly. What surface is shown in the first illustration? (Hilly.) In the second illustration? (Flat).
Explain why the plains received such names? (A flat plain has a level surface; a hilly plain has hills.)
Open your textbooks to pages 90-91. Find on the map all the plains on the territory of our country, name them. Pay attention to the color they are shown on the map. (Plains on the map are indicated in green or light yellow). Slide 10. (Physical map, plains, will be highlighted.) (East European, West Siberian Plain, Central Siberian Plateau.)
Why is the Central Siberian Plateau indicated on the map in yellow and green? (There are elevations). The elevations on the plain are hills. Slide 11 (“Hill”) appears. The following parts are distinguished in the structure of a hill: the sole (or foot) is the lowest part of the hill, this is the place where it begins; apex is the highest place. There is a slope between the top and the bottom . It can be flat and steep. An animation appears on the slide - parts of the hill.
A trained student reads A. Shatalov's poem "Hill".
I climbed the hill, looked around -
At this dark hour I did not recognize the plain.
Fog floated from the swamp, approaching the meadow,
And the tops of the trees rose above him.
And below, in the distance, at the foot of the hill,
Where in the ravine the stream meandered and played,
Everything has already been taken over and ruled by darkness.
I went down there, stepping carefully,
The fresh smell of grass and evening fog,
Lonely sobs of sleeping birds -
The night was created for us by an intoxicating intoxication.
I swayed and sat down under a spreading linden tree.
IV. Work in a notebook. In your notebook on page 32, label the parts of the hill. Check with your seatmate.
V. Physical education minute.
Children walked through the forest, ( Children march in place)
Nature was observed. ( The palm is applied to the eyes)
Looked up at the sun (Raise their heads up, "reach for the sun")
And their rays warmed them.
Butterflies were flying
They flapped their wings ( Waving their arms)
Let's clap together, ( Clap your hands)
Let's stomp our feet! ( Stomping feet)
We had a good walk, ( They march, take a breath and exhale)
And a little tired! ( Children take their seats)
VI. Continue learning new material.
We talked about elevations on plains - hills. But, in addition, on the plains there are depressions with steep slopes - these are ravines. The teacher shows slide 12 (“Ravine”).
On the plains, people plow the land and plant crops. But sometimes on the plains there can be not only elevations, but also depressions. Such depressions are ravines. How are they formed? The prepared student speaks.
"The formation of a ravine begins with a small pothole. Melt and rainwater wash it away, and the ravine gradually increases. Gullies can be shallow, several meters deep, and deep - several tens of meters. The bottom of a ravine is always narrower than its upper part. Along the bottom of the ravine there is often a river or stream flows.If a lot of grass and shrubs grow along the edges of a ravine, then it turns into a swamp.
Gullies cause harm to humans because they destroy the top, fertile layer of soil. To combat the growth of ravines, people plant trees and shrubs along their edges. The roots of plants prevent the soil from deteriorating."
Video clip 13. “On how elevations and depressions of the earth’s surface appear.”
Guess the riddle.
In the hot summer I stand,
I get the winter out with a hat.
What do you think this is? (Mountain.)
That's right, it's a mountain.
The teacher shows slide 14 "Mountain".
Look at the image on the slide, what part of the earth's surface do you think is called a mountain? (Elevations.) Mountains are very uneven areas of the earth's surface that rise greatly above the surrounding area.
On the tops of the mountains it is very cold and there is snow.
Slide 15. (Parts of a mountain) Each mountain, like a hill, has its own parts, try to name them. (The sole or foot, the slope and the top.)
Open the physical map of Russia in the textbook p. 90-91. Find mountains on it. What color are the mountains on the map? Slide 16. (Physical map, highlight mountains using animation) What mountains did you find on the map? (Ural and Caucasus mountains.)
Have any of you been to the mountains? Listen to my story about the Caucasus Mountains. Slides 17 will help you imagine this better. (Caucasus Mountains)
The main mountain region of the Caucasus is the Greater Caucasus - a grandiose mountain rise consisting of numerous ridges. It stretches from northwest to southeast. Approaching the Caucasus Range from the north, another 200 kilometers away you see on the southern side of the horizon the outline of Elbrus (slide 18), which glows white on a clear morning above the plain. The height of Elbrus is 8848 meters. This is the highest mountain. Slide 19.
The vegetation of the Caucasus Mountains is a complex world in which altitude plays a big role. Every 200 meters rise in the mountains means a drop in temperature by 1-2 degrees. Therefore, moving towards sky-high heights, we observe a rapid change in vegetation and finally find ourselves in an area of eternal snow, where frost and snowstorms are as fierce as in the Far North of our country.
The North Caucasus is one of the main resort centers in Russia. Anapa is the largest children's resort with a comfortable sandy beach. (Slide 20)
Another largest resort is Caucasian Mineral Waters in the Stavropol region. (Slide 21). Pushkin was here twice. Lermontov was exiled here. Here, in Pyatigorsk, in 1841 he was killed in a duel. Many memorable places in Pyatigorsk are associated with this Russian poet. Listen to poems in which poets describe the Caucasus.
A trained student reads an excerpt from A. Pushkin’s poem “Prisoner of the Caucasus.”
In the early morning cool
He fixed his curious gaze
To remote communities
Gray, ruddy, blue mountains.
Magnificent paintings!
Thrones of eternal snow,
Their peaks seemed to my eyes
A motionless chain of clouds.
And in their circle is a two-headed colossus,
Shining in an icy crown,
Elbrus is huge, majestic
White in the blue sky...
A trained student reads M. Lermontov's poem "To the Caucasus".
Greetings, gray Caucasus!
I am no stranger to your mountains.
And for a long time I dreamed from then on
All the sky of the south and the cliffs of the mountains.
You are beautiful, harsh land of freedom,
And you, eternal thrones of nature.
With these beautiful lyrical lines we will finish our acquaintance with the mountains.
VII. Lesson summary
What forms of the earth's surface have you become familiar with? (Mountains and plains) what types of plains are there? (Flat and hilly). What shape of the earth's surface is called a hill? What shape of the earth's surface is called a ravine? What mountains of our country can you name? What plains do you know?
As a result, a diagram appears on the board. "Shapes of the Earth's Surface." Slide 22.(diagram)
Homework: Slide 23.
- An option is to solve the crossword puzzle.
- An option is to make a drawing in a notebook.
The textbook pp. 76-78 will help you complete the task.
Slide 24. (Thank you for your work in class!)
Solve the crossword puzzle.
| G | |||||||||
| O | |||||||||
| R | A | V | n | And | n | A | |||
| A | e | ||||||||
| R | |||||||||
| P | O | d | O | w | V | A | |||
| V | And | ||||||||
| l | e | R | m | O | n | T | O | V | |
| A | A | ||||||||
| G |
Horizontally:
Large expanse of flat surface. (Plain)
The lowest part of the hill. (Sole)
Russian poet who died in the Caucasus. (Lermontov)
Vertically:
An elevation more than 200 meters above the surrounding area. (Mountain)
The lowest point of the hill. (Vertex)
A winding, sharp decline in terrain. (Ravine)
Shapes of the earth's surface
Plains- these are flat or almost flat areas of the earth's surface
Mountains- These are very uneven areas of the earth's surface that rise greatly above the surrounding area.
Almost all mountains arose as a result of the movement of tectonic plates. They come in three main types - folded, block and domed. Most of the highest mountains, for example, the Himalayas (Asia), are folded; they extend over vast distances, forming chains. Some mountains are still growing, others are collapsing, or undergoing erosion, under the influence of atmospheric phenomena.
Parts of mountain and hill
The parts of a mountain and a hill are called the same, there are three of them in total: the top, the slope and the bottom, or, in other words, the foot. The slope can be steep or gentle. The difference between a mountain and a hill is its height.
Draw a mountain and label its parts

What is the surface like in your area? Draw or stick a photo
Plains |
Mountains |
 |
|
High in the mountains, you can see some of the most stunning, awe-inspiring landscapes on our planet: jagged, snow-capped mountain peaks, deep gorges, sweeping valley glaciers, rushing rivers and watercourses. Mountains constantly challenge the human desire for adventure.
Preview:
Topic: “Shapes of the earth’s surface.”
The purpose of the lesson:
- Introduce types of earth's surface
Tasks:
- To develop the ability to identify various shapes of the earth's surface;
- Introduce the structure of hills and mountains;
- Develop the ability to navigate the terrain.
During the classes.
1.Motivation for educational activities.
Good afternoon guys. We are starting a lesson about the world around us. Say hello to our guests.
1-2-3-4-5! The sun is shining again!
1-2-3-4! Everything is beautiful in this world!
1-2-3-4-5! We can reason!
The world around us is interesting to know
Are we ready to unravel its secrets and riddles?! (Ready!)
Have a seat!
Today I brought you this bag for class. What is it called?
Let's see what's in it.
Why do people travel?
For discoveries
Which of you today is ready to go on a journey to gain new knowledge?
I really want each of you to make a discovery today
What they will be - big or small - is different for everyone.
What kind of person should we be in order to receive discoveries? What should I be like?
2.Updating basic knowledge.
- What have we already learned so that we can go on a journey?
Let's play the game “Believe it or not.” If you agree with the statement, then you clap. If you don’t agree, then stomp.
- Do you believe that the horizon is the earth's surface that we see around us? (Yes)
- Do you believe that the boundary of the horizon where the sky meets the earth's surface is called the horizon line? (Yes)
- Do you believe that the main directions of the horizon are NE, SE, SW, NW? (No)
- Do you believe that a compass is needed to navigate in space? (No)
- Do you believe that if you stand with your back to the sun at noon, then north will be ahead, east will be on your left, and west will be on your right? (No)
So, I see that you are very well prepared for the trip.
Let's hit the road!
3.Formation of new knowledge, skills and abilities.
(slide) Traveling around the Earth, people noticed that its surface is not the same everywhere; there are flat areas, hills, and depressions on the Earth. Look at the screen.
What groups can these photographs of the area be divided into?(Slide)
Try to determine the topic of the lesson.
Lesson topic: Shapes of the earth's surface.(Slide)
And experts will help me in determining the shape of the earth's surface.
Who has seen the mountains?
Who has seen the plains? What area do we live in?
Do we know everything?
Let's set tasks for the lesson: What would you like to know?
- Let's find out what forms of the earth's surface there are,
- let's learn to compare them,
- Let's learn to notice and appreciate the beauty of nature.
Look at the screen. During our journey we will fill out the following table: the shapes of the earth's surface. ( Slide)
(slide) Look at these photographs and try to name the main shapes of the Earth's surface.
What discovery have we made?
There are mountains and plains on Earth
We supplement our table with new terms: mountains, plains. ( Slide)
And an expert will tell us about the plains.(slide)
Since ancient times, people have settled on the plains. Cities are built on the plains, roads are laid, cattle are grazed, grain is sown. Vast areas of the plains are occupied by deserts and forests.
Do you think all plains are the same?
Try to define a plain. ( Slide)
Let's listen to an expert.
Plains are different. Flat and hilly.
Filling out our table - flat and hilly (Slide)
Flat ones have a flat surface, hilly ones have hills.
A) Working with a physical map of Russia.
How do you think about how to find out on a map which terrain is flat or mountainous? Let's find and show the plains of our country. A physical map of Russia is on your desk.
What can you find on the plain? (elevation – hill)(Slide)
I suggest you listen to an expert.
Any hill can have separate parts. Try to identify and show them yourself.
Summit - the highest point
Sole - beginning of elevation
Slope is the distance between the bottom and the top. Slopes can be steep or gentle. (Slide + layout)
Reading from the textbook. p. 78
Find in the textbook the definition of what a ravine is.(slide)
Let's fill out the diagram.(Slide)
What do you think a ravine is? How was it formed?
Physical education minute.
We'll rest a little.
Let's stand up and take a deep breath.
We'll reach the mountain now.
Here is the bottom, here is the top,
Left slope and right slope.
We'll climb to the top
And let's look around!
Imagine that you are a mountain.
Show the top, bottom, slopes.
Working on the topic of the lesson.
Well, of course, this is a miracle!–
It's been a century now
Even in the hottest summer -
There is snow on its top!
That's right, we ended up in the mountains.(slide) Look how beautiful it is there!
Listen to how Nikolai Ivanovich Sladkov described the beauty of the mountains.
Working from the textbook. pp.80-81
Reading aloud.
What can you tell us about the mountains?
Who can define mountains?
What will the experts tell us?
Mountains are very uneven areas of the earth's surface that rise greatly above the surrounding area. (Slide)
You rarely see a single mountain (Slide), most often the mountains are located in rows - mountain ranges. (Slide)
Let's fill out the diagram. New geographical concepts - single mountains and mountain ranges.(Slide)
Now let's look at the hill and the mountain.
Find commonalities and differences.(Slide)
Let's find mountains on the map of our homeland. The oldest mountains are the Ural Mountains. The Ural Mountains appeared about 600 million years ago.The length of the Ural ridge is more than 2000 kilometers.
And in the Caucasus Mountains there is the largest mountain in Russia.
Elbrus is the priceless pride and heritage of Russia.
Independent work in groups. (talk about the rules for working in groups)
We have studied the basic shapes of the earth's surface. And I suggest you complete tasks, each group has its own.
Group 1 - crossword
Group 2 – match the concept with the definition
Group 3 - label the parts of the hill and mountain
Group 4 – fill in the missing concepts
Our journey has come to an end.
Where have we been?
I think our lesson has become a lesson of discovery for you.
Reflection.
I want to know how you liked the lesson. Our journey has come to an end.
Think and determine the quality of your work in class.
In different places of the classroom there are illustrations of “Plain”, “Hill”, “Mountain”,
Those guys who agree with the statement:
- “I wasn’t interested in the lesson, I didn’t listen attentively, I didn’t understand the lesson material,” attach a sticker to “Plain.”
Those students who think:
“I listened carefully, but I didn’t understand everything; I won’t be able to use the knowledge gained in the lesson in life,” attach a sticker to the “Hill.”
Those students who are sure that “I listened carefully. I got it. I can use the knowledge I learned in class,” attach the sticker to “Mountain.”
Almost all the flags were on the mountain, which means you did a great job, and now you can handle any mountain.
Lesson summary.
What are mountains?
Do you think the word MOUNTAINS is used only in this geographical sense - these are very uneven areas of the earth's surface that rise greatly above the surrounding area?(In life this is a polysemantic word. Mountains are heights, obstacles that need to be overcome)
I wish you that in your life you will be able to overcome all the mountains, all the peaks were on the shoulder.
I would like to quote the words from the song by Vladimir Vysotsky
The only things better than mountains are mountains
Which I have never been to before!
May you visit all the mountains you want in your life. And conquer the peaks that you have in mind. And no matter what height you find yourself at, remain, first of all, a person - kind and reasonable!
APPENDIX (WORK IN GROUPS)
GROUP 1 – CROSSWORD
Solution to the crossword puzzle "Shapes of the Earth's surface"
Horizontally:
2. Plains that have a flat surface are... plains.(flat)
4. Hills on the plains are called...(hills)
6. Flat or almost flat areas of the earth's surface.(plains)
8. Mountains arranged in rows.(mountain ranges)
Vertically:
- Plains with hills on the surface.(hilly)
3. These wonderful giants
They wear stone caftans.
White hats on top of heads,
The top reaches the clouds.(mountains)
5. Depressions on the earth's surface with steep, crumbling slopes.(ravine)
GROUP 2 – RELATE THE CONCEPT WITH THE DEFINITION
GROUP 3 – LABEL THE PARTS OF A HILL AND MOUNTAIN
Shapes of the Earth's Surface
The world
2nd grade
"School of Russia"

1. Name the main sides of the horizon. 2. Draw a diagram of the movement of tourists (one cell – 1 day).
- The traveler left the point A and walked north for two hours, then west for 2 hours, north for 2 hours and east for 2 hours. Then he made a halt (point IN on the diagram) and went further;
- It took 1 hour to go north, 1 hour to go east, 2 hours to go south and 3 hours to go east. Here he spent the night (period WITH ). In the morning I went further;
- It took 1 hour to go north, 1 hour to go east, 4 hours to go south and 2 hours to go west. The traveler was tired and made a halt (point D );
- Then he went further: he walked north for 2 hours, west for 1 hour, south for 2 hours, west for 2 hours... And he returned home.

Card No. 1

Card No. 2
Fuse
Frame
Magnetic needle
Magnetic needle

Card No. 3

Forms
terrestrial
surfaces

R A V N I N A
PLAIN is a flat or almost flat area of the earth's surface.

R A V N I N S
hilly
flat
hilly

Elevations on the plain are hills .

Identify the parts of the hill
VERTEX
SLOPE
TOP SLOPE SOLE (FOOT)
SOLE (FOOT) )

Ravines are depressions with steep slopes, washed away by rain and snow waters .


Job according to the textbook
- Open your textbook to page 79.
- Look at the hill and the mountain in the diagram and compare them with each other.
- What are the similarities and what are the differences?

A mountain and a hill have the same parts.
Vertex
Slope
Sole
A slope is that part of a mountain or hill that
which is located between
sole and top.
There are slopes cool or flat.
Sole (foot) is the place
Vertex – the highest part
where a mountain or hill begins.
hill or mountain.

What is the difference between a hill and a mountain?
Height up to 200 m
Height more than 200 m
In the mountains there are rock outcrops on which nothing grows, but the hills always have soil and are covered with vegetation.

Mountains differ in height.
High
(more than 2,000 m)
Average
(from 1,000
up to 2,000 m)
The height of the mountains varies. Some of them rise several hundred meters, others several kilometers.
Low
(up to 1,000 m)

Mountains are giants
The highest mountain in the world is Everest, height 8848 m.
The highest mountain in Russia is Elbrus, height 5642 m.
The highest mountain in Kamchatka is Klyuchevskoy volcano, height 4850 m.


FORMS OF THE EARTH'S SURFACE
PLAINS
MOUNTAINS
HILLY
FLAT
ROVIES HILLS
HILLS
ROVIES

“I believe it or not”
Plains, mountains, hills, ravines are the forms of the earth's surface.
Plains are flat or almost flat areas of the earth's surface.
The mountains are very convenient for farming.
Most often, mountains are located in rows - mountain ranges
The highest part of the mountain is the base.
There are slopes between the top and the bottom.
Our region has a mountainous surface.
The height of the mountain is more than 200 m

Crossword "Shapes of the Earth's Surface"

Information sources
Presentation Template
Physical Map of Russia
Anthill
Ravine Ravine
Moss On Tree
Task "Chain" Exercise « Puzzles »
Birch
Hills Hills Hill
flat plain
Game crossword
Poster “Shapes of the Earth’s Surface” Restore the text
Plain Plain
Ravine video
Ship on the horizon
Ural mountains
Mountains
Golden Mountains of Altai
The highest mountains in Russia Map
Video Music of the Mountains: Caucasus

The presentation was prepared by a primary school teacher at MBOU Secondary School No. 22
city of Staraya Kupavna
Klimenkova Tatyana Aleksandrovna